The DBTable attribute (Location class)
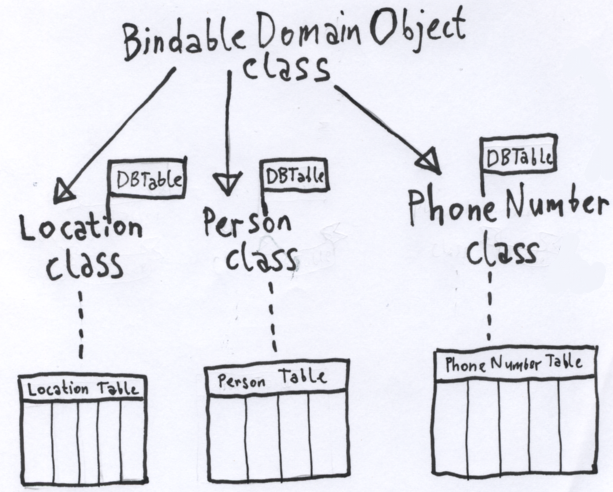
The [ DBTable ] attribute controls where class instances are persisted. The domain class attributed with [ DBTable ] and all their children get their own class. This mechanism is explained briefly here: FIXME, a more comprehensive discussion is the section FIXME in the PhoneBook tutorial.
For this PhoneBook sample, our hierarchy is boring – no subclassing of domain object classes here. We give each class it's own [ DBTable ] attribute, thus its own table:
We don't have many options here, but an alternative would be to introduce an abstract base type PhoneBookBase, derive all PhoneBook domain classes from it and persist them all in the same table:
As you see, the three sub-classes inherit the DBTable attribute from abstract PhoneBookBase class. They share a DBTable attribute, so they share a table. The column names are merged. For this scenario it is useful to have that DBColumn}}mentioned above, by the way. Without it, we would get column name clashes, because both the {{Location class has a property Number, but also the PhoneNumber class.